it service delivery infrastructure
introduction#
As with Nagios, i dived into Combodo iTop solution.
Even though it is not a host monitoring solution, it can be a part of a monitoring infrastructure.
I had harder time getting into it due to the notions to lean & to consider, inside & outside itop to use it properly.
So once again, i’d be very grateful if you’d consider correcting me if i said someting wrong.
glossary#
Defining mandatory acronyms for this post.
ITSM - IT Service Management
Type of tool usually used by companies to organise & deliver their IT services to their departments or to other companies. They can integrate monitoring tools or a help desk ticketing system for example.
CMDB - Configuration Management Database
Term to define a database used to store & organise the hardware items & the software assets of a company or someone.
ITIL - Information Technology Infrastructure Library
Set of relevant IT practices describing processes, procedures or actions for IT related operations like system administration or itsm management.
presentation#
Combodo is a 13-year-old french company who created itop, an open source, itil based, itsm & cmdb solution.
They are a profit based company, they created 2 non-free versions of itop for business purposes: essentials & professional/enterprise.
They also provide free & non-free external software to enhance itop utilisation like a front-end customiser or a network related manager; as weel as consultants.
itop is typically used by the IT department of a company to organise services & implement a help desk ticketing system to the other departments.
It is also used by companies to deliver IT services to other companies as a service provider.
understandings#
Reviewing my understanding of itop’s main features.
fundamentals#
itop is based on apache, php, graphviz & mysql. However, it can run on nginx instead of apache with extra work.
The documentation is made for anyone who is susceptible to use itop.
cmdb#
The cmdb is the core of itop.
The cmd works with Objects, which are groups of Instances sharing the same patern.
(considering the “Persons” object, each instance of this object would have the same patern: a name, a surname, an age etc.)
The cmdb can receive a populated *.csv file to create multiples instances of an object at once. (instead of entering one by one every member of a company for example)
itop can receive custom objects but their implementation is not guided. The default ones are created without instances.
Objects & instances are stored in the MySQL database.
itsm#
The itsm is integrated with the ticket management system & will be described using the itil way.
When installing, itop proposes two ways to implement it: to deliver services to departments or to other companies; saw at the end of the presentation.
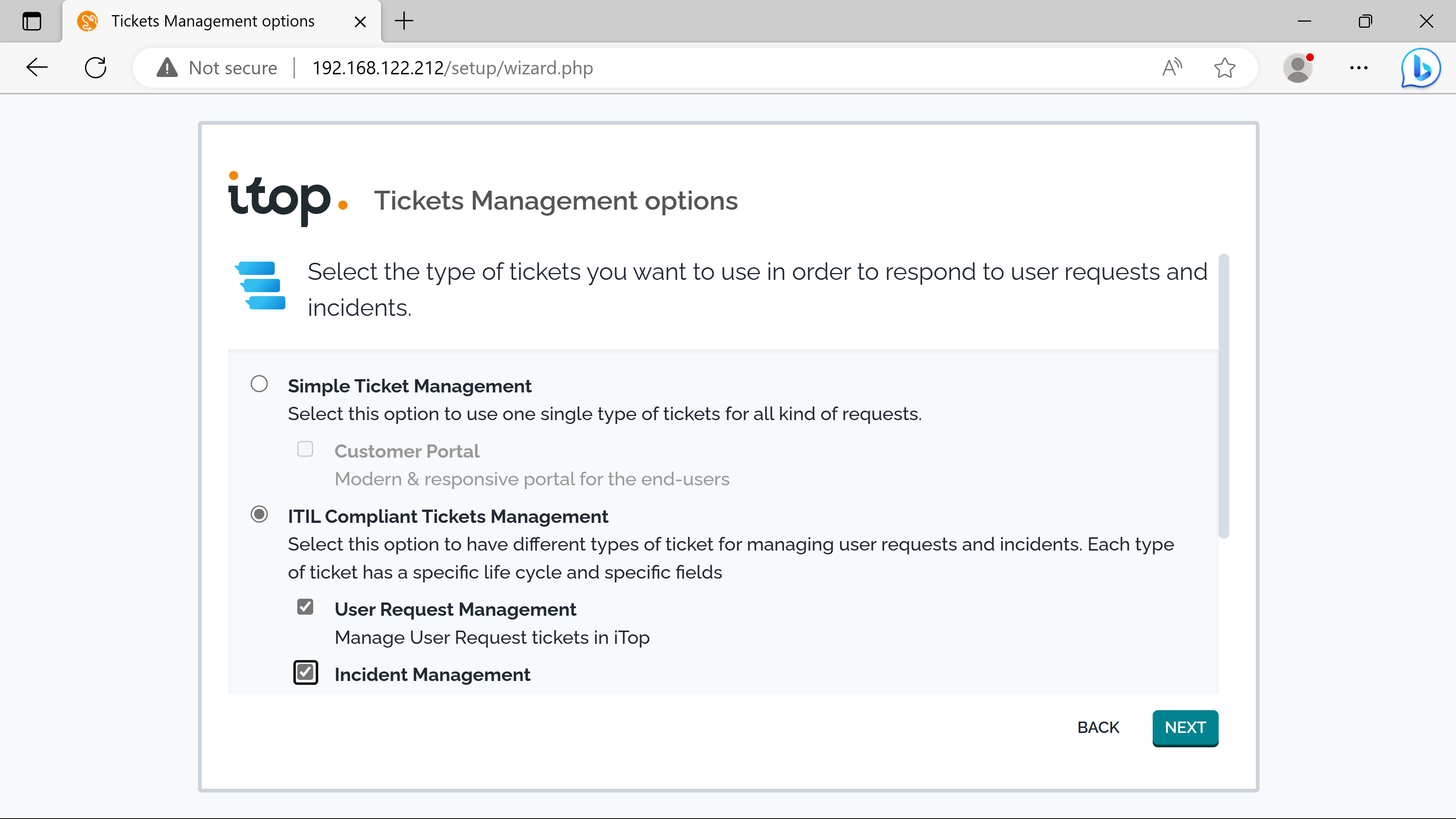
The itsm provides two types of tickets for end users: Users requests & Incidents.
Mandatory objects are needed to use them: Services, Contracts & SLAs.
Here are their purposes & how they are related.
Services
Are defining what is provided by the service provider (IT department or company). Called to generate incidents or to supply users requests. Providers contracts are required.Contracts
Splited inCustomer&Providercontracts. Customer one defines service(s) provided to/pucharsed by the customer + theSLAs. Provider one links internal ressources (CIs) used for the service(s) provided.SLTs - Service Level Target
Define metrics agreements between customers & providers. Two by default: TTO - Time To Own: time to take a ticket into account & TTR - Time To Resolve a ticket after creating.SLAs - Service Level Agreement
Group ofSLTsdefining the agreement between a provider & a customer for a given set of services.
When a customer creates a ticket, it can select the service amongst the list of services defined for this customer.
Tickets deadlines are computed depending on the SLA signed with the customer.
default objects#
Native objects in itop are created during the installation process.
They should be used because related to itop principles.
The mandatory objects are covered here, many more can be used & discovered exploring itop.
Organizations
Can be used for two purposes: name the different departments of a company when itop is used to deliver IT services within a company, or name the different companies a company is delivering IT services to.Locations
Are used to group objects by geography - servers, organisations etc. A hierachy can be applied, locations can be linked to parents locations (example: inside the company A, there is room A & room B in which have differents servers in racks A & racks B)Persons
Define the persons contacts & responsabilities regarding the IT services delivered. Can be deployed usingProfilesto quickly assign permissions (to the members of a department or a company).Teams
Usefull to define permissions easier - all the HR & finance teams can access to… -. Can also help the customer to communicate using the ticketing system.CIs - Configuration Items
Describe hardware devices: racks, pdus, network devices, servers, personal computers, hypervisors, vms etc. Templates are available for a large type of CIs.Software Installed
Present to easily index software installed on devices, licences & so on.Services
Object used to define what actions or access is delivered as a service to a customer. Can be subcategorised - service A contains sub-service B & sub-service C.
objects agencement#
Objects are related to each others by different means.
I made graphs to show the links between them, or tried to.
Graphs are generated using the following rules:
- Rectangles are highest objects.
- Rounded objects are those receiving links.
- Text in lowercaps are instructions, uppercaps are objects name.
Persons integrate Teams according to their Roles.
Teams belongs to Organizations.
Organizations are linked to Locations.
Regarding to only these objects, links can be created.
(Persons -> Teams -> Organizations -> Locations)
Before doing that, there are links between objects covered in default objects.
Organizations are owning CIs. CIs are exposed to Services & are ruled by Provider Contracts. They can be related to Documents & appear in Tickets.
Relations for Documents.
All objects have relations to others at some point by different ways.
In addition to this, objects’ instances have their own properties changing the relations between objects according to their needs.
It would be meaningless to create decent relations graphs for all objects, since their dependencies & relationships are to massive & could change each instance.
Even though this graph seems valid for the most part, itop has many more objects than the ones covered. Links between them should be discovered & created using the frontend.
implementation#
This sections will implement itop following a companies charts & an arbitrary infrastructure.
companies charts#
itop will be used by two companies: Company A which is the service provider & Company B who use their services.
Here is the Company A agency graph.
Here is the Company B one.
All persons in the two companies will have access to an itop interface (in reality it is not necessary).
requirements#
Here is the itop hardware recommendations from their documentation.
| Activity | Recommendations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
infrastructure#
There is 13 people who will potentially use itop in the two companies combined (< 50). The number of CIs will be under 50'000 & the tickets/month under 200.
The all-in-one server will be chose with itop & a MySQL server installed.
Here is the network infrastructure that will be used.
2vCPU 4GB) db-server[(MySQL DB
10GB)] itop(itop Community) apache-a(Apache Server) end wan{WAN} --- router-a & router-b router-a ---|192.168.122.0/24| switch-a switch-a ---|192.168.122.212| itop-server itop-server -.- db-server & itop switch-a ---|192.168.122.111| apache-a router-b ---|192.168.1.0/24| switch-b switch-b ---|192.168.1.1| consumer-pc switch-b ---|192.168.1.2| apache-b
The Company A is providing an apache web server from their LAN as a service & monitor an other one from the Company B LAN.
installations#
I made an installation scripts for itop community & for a mysql server according to itop requirements.
(yes, i could saved a lot of time not doing this, but foss)
Both scripts are interactive & made for debian - tested on debian 11 & 12, source code is on Github.
The itop server installation can be done running the following commands.
mkdir itop_install && cd itop_install
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xeylou/itop-tour/main/debian-itop-install.sh
chmod +x debian-itop-install.sh
./debian-itop-install.sh
Here to install the mysql server.
mkdir mysql_install && cd mysql_install
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/xeylou/itop-tour/main/debian-mysql-install.sh
chmod +x debian-mysql-install.sh
./debian-mysql-install.sh
An external mysql database can be used without this installation script, an full privilieged user for this database is needed to use itop.
The installation can be resumed at http://192.168.122.212.
(highlighted forms are clicked/changed values)
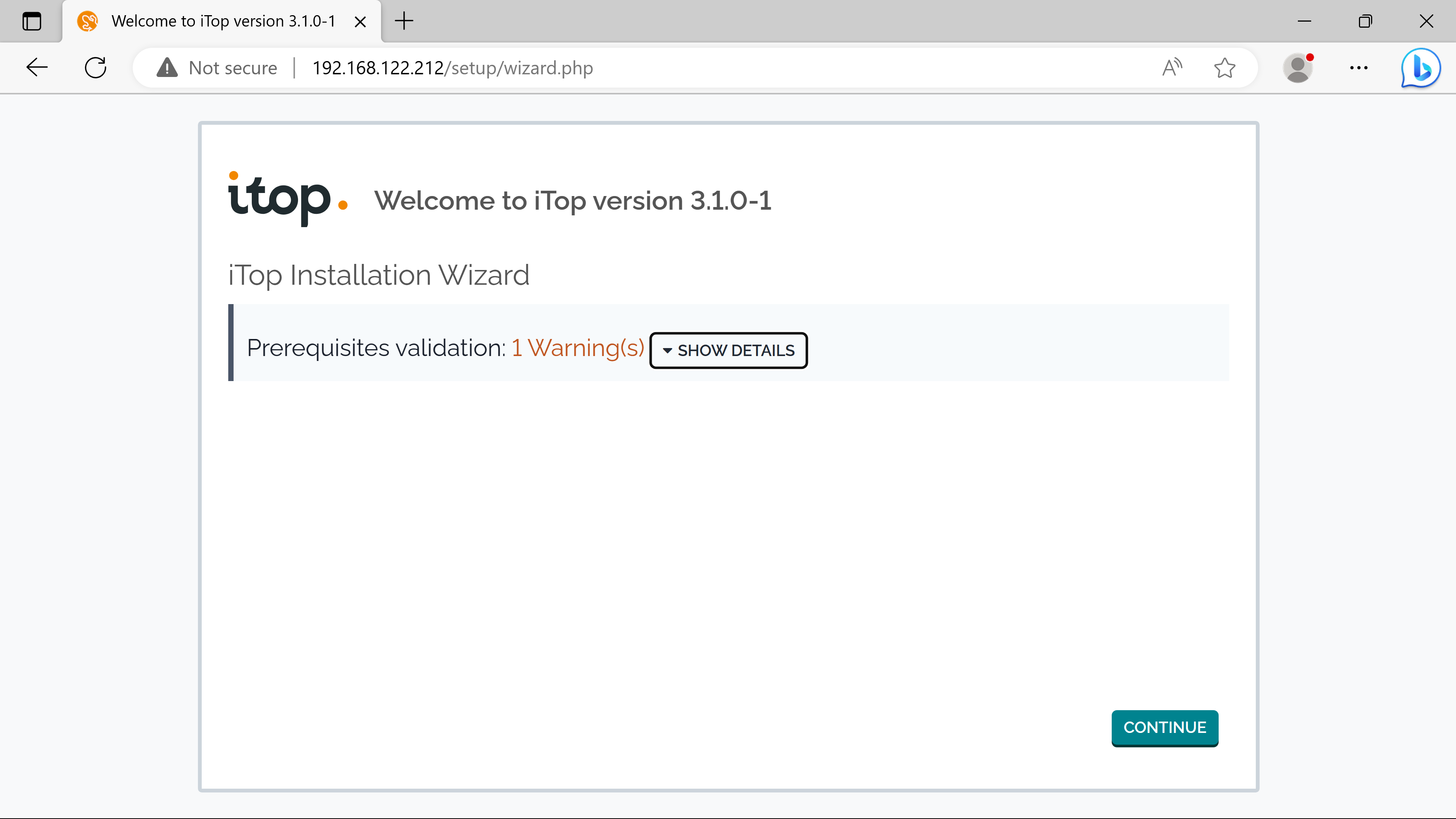
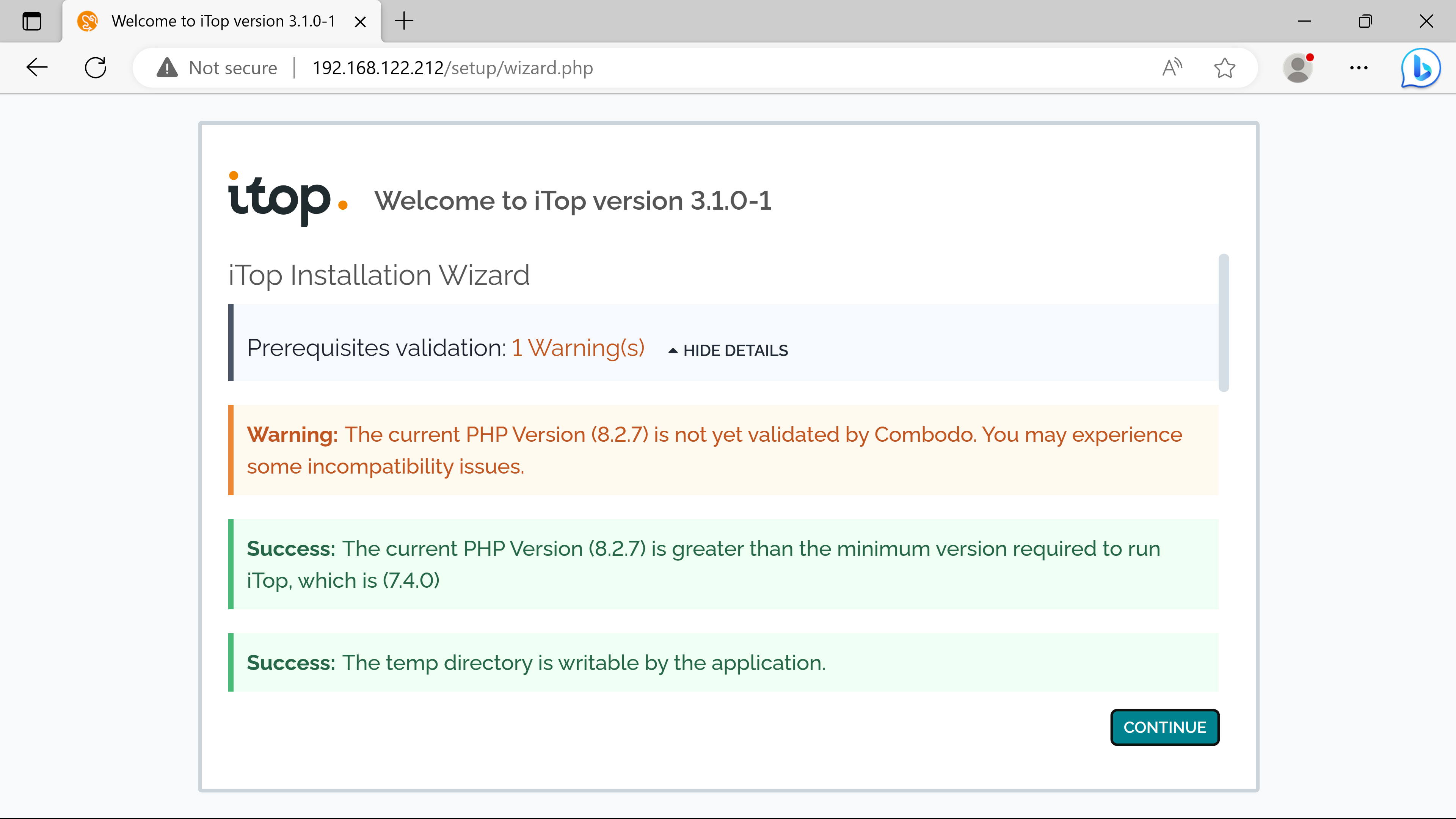
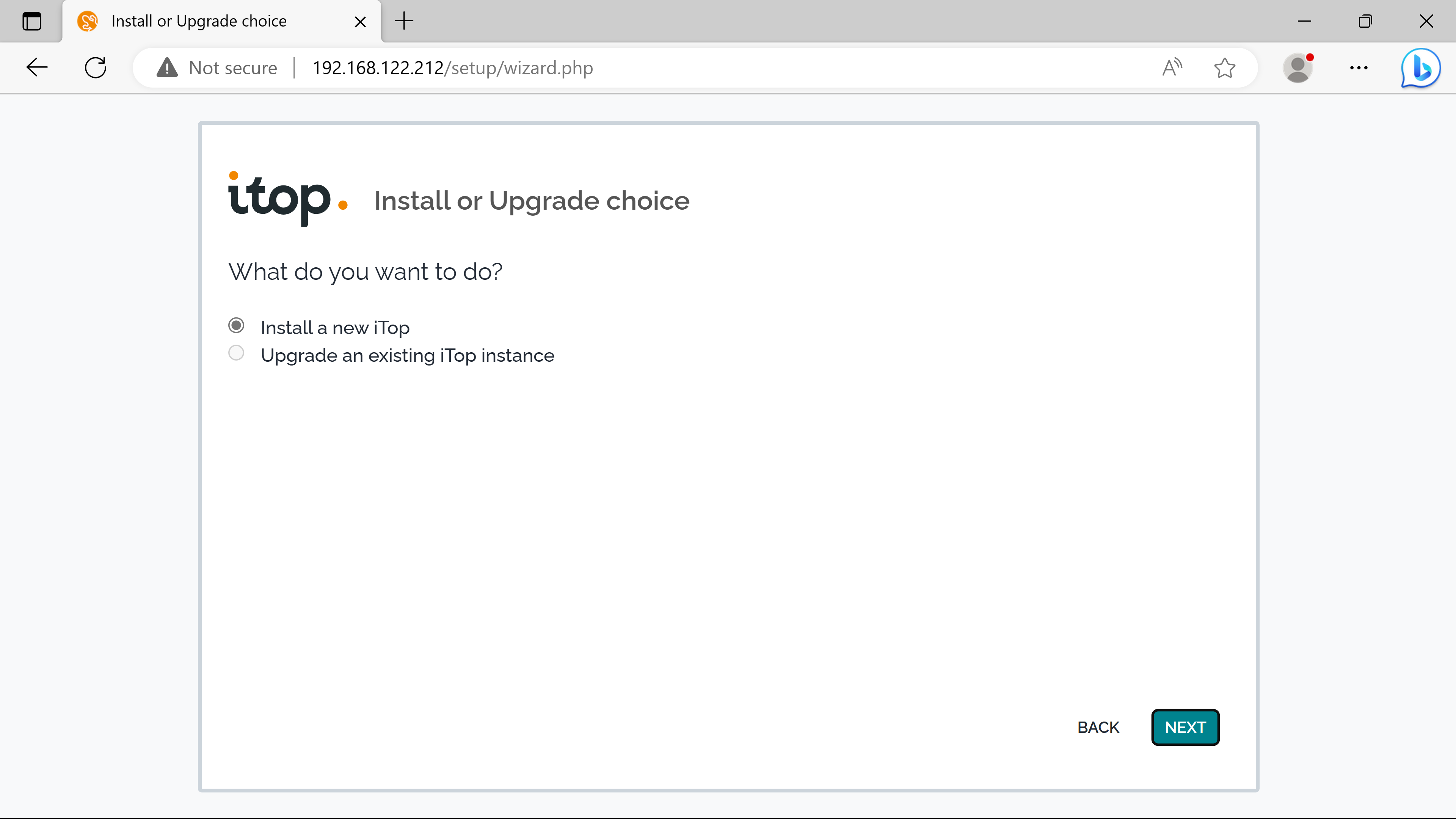
Server Name is localhost because the itop instance & the mysql server are on the same host - can be replaced by the ip address of the external mysql server if using the seperate solution.
The Login & the Password was created during the debian-mysql-install.sh script process - asked at the beginning -.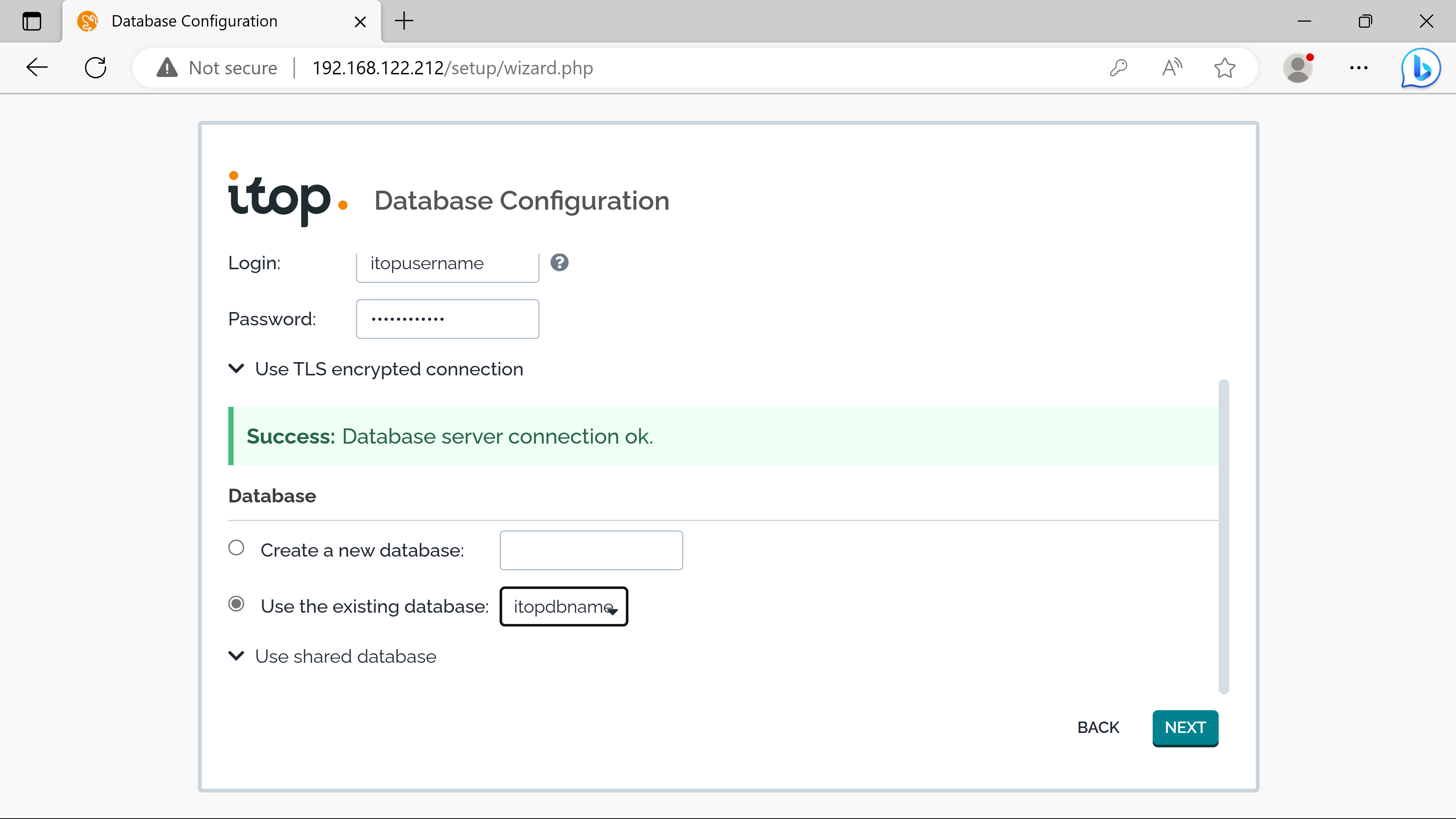
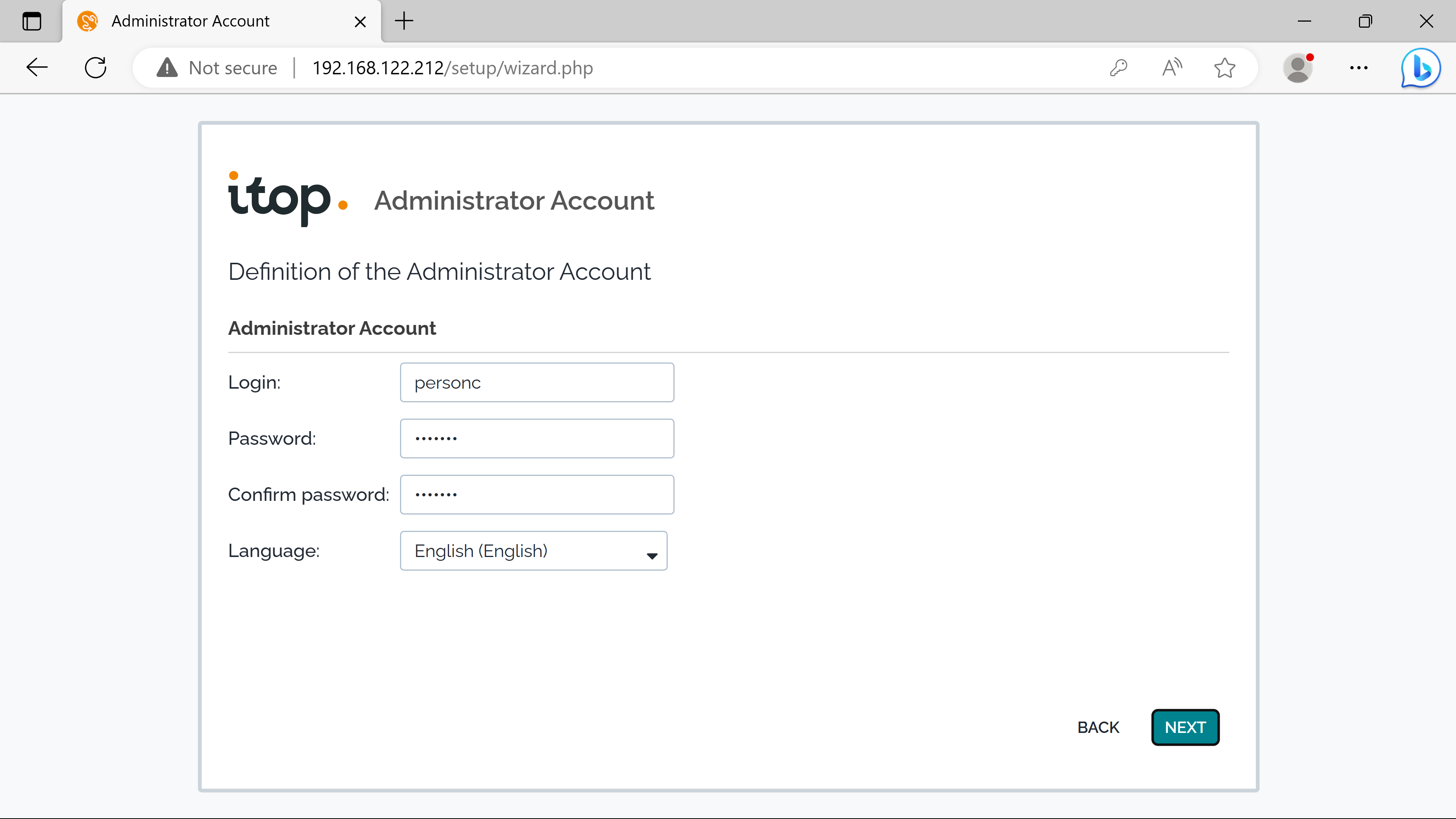
Person C will have admin privilieges for this itop instance, since it is the Technical Manager. (can add more admins after)
The Language set is for this user only.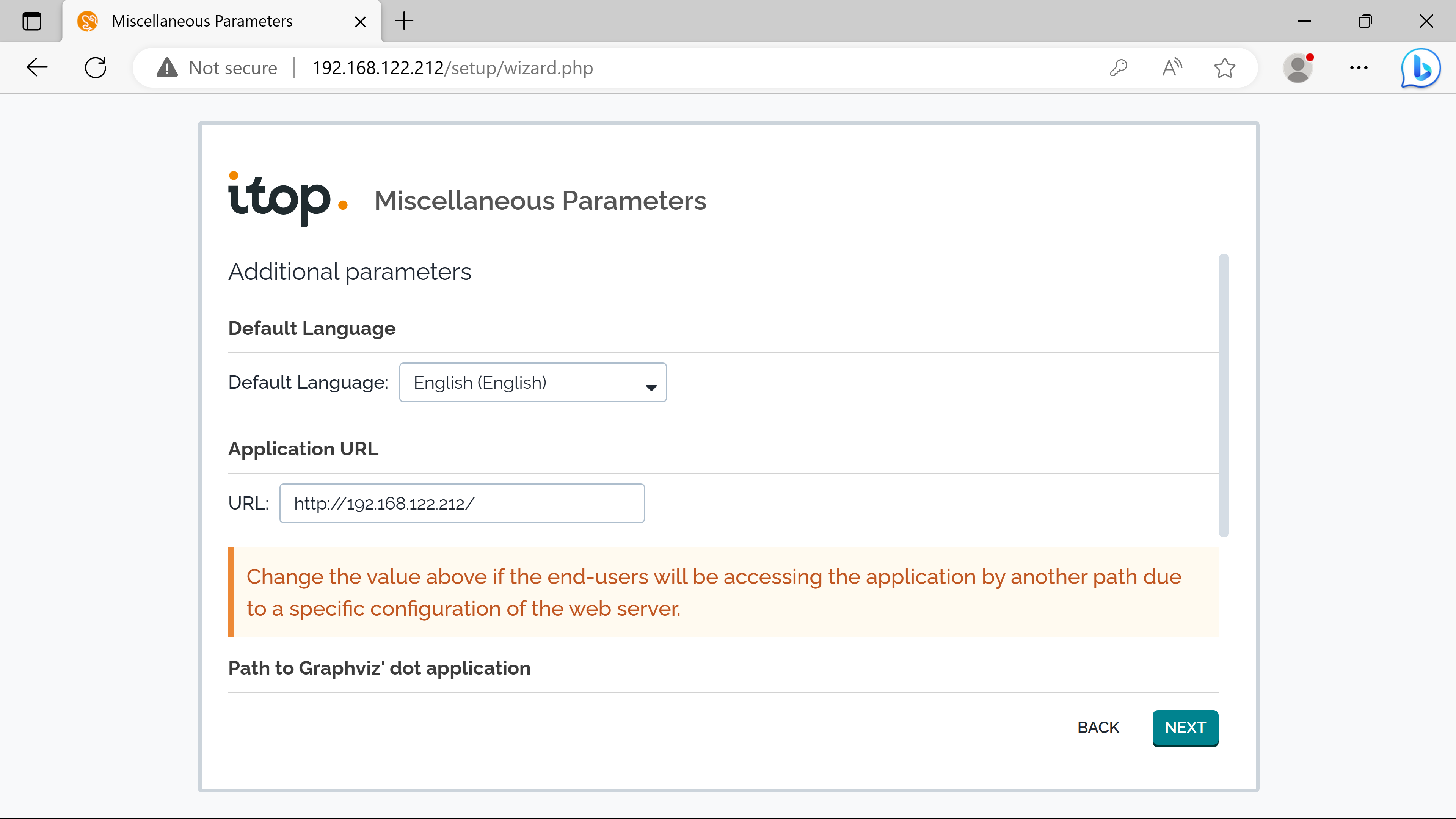
Default Language for all users can be changed. Can also be changed by individual users after deploying.
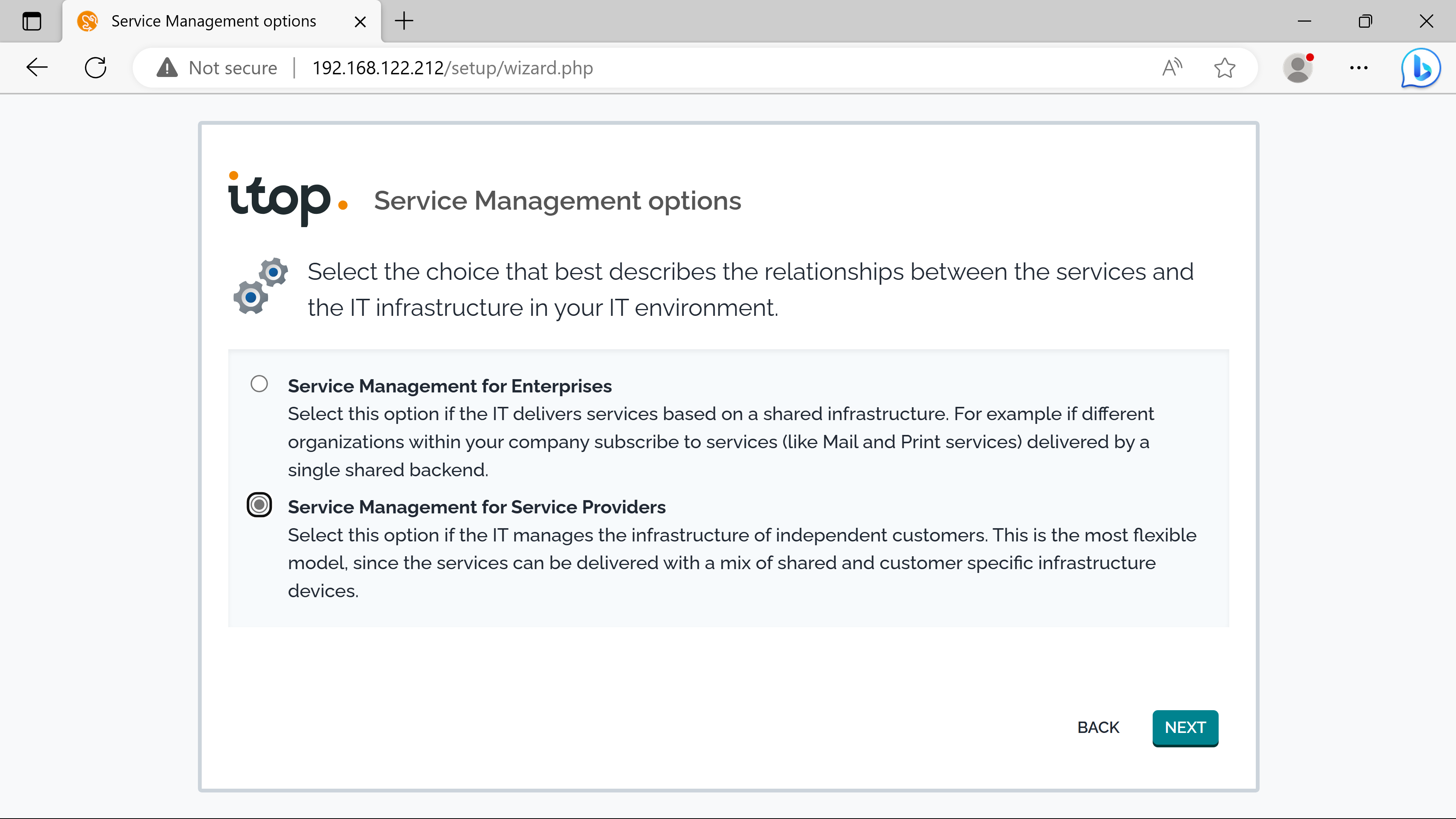
Company A acts as a service provider, the second option is chose. The first option should be kept if delivering IT services to company departements.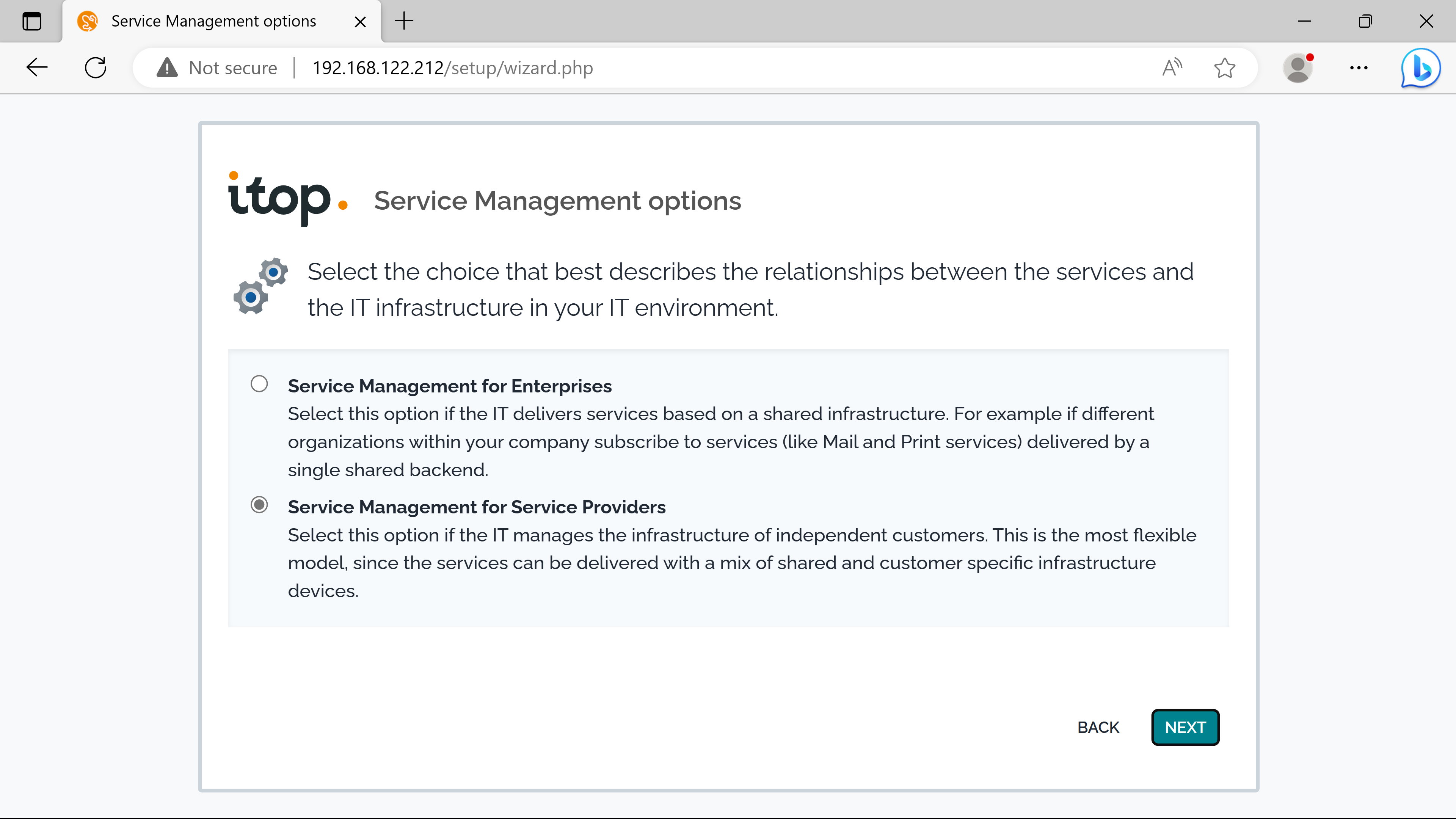
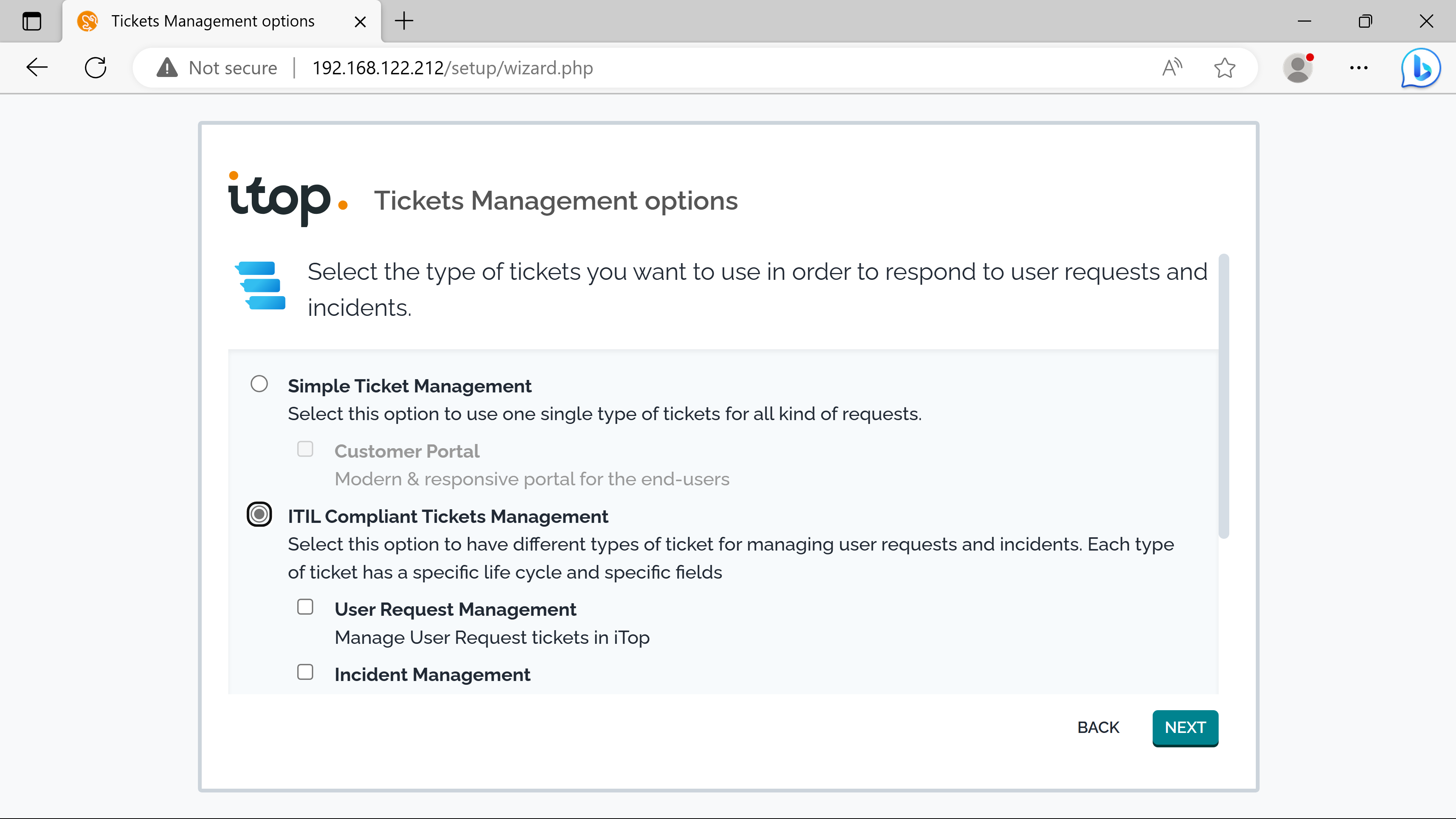
SLTs & SLAs.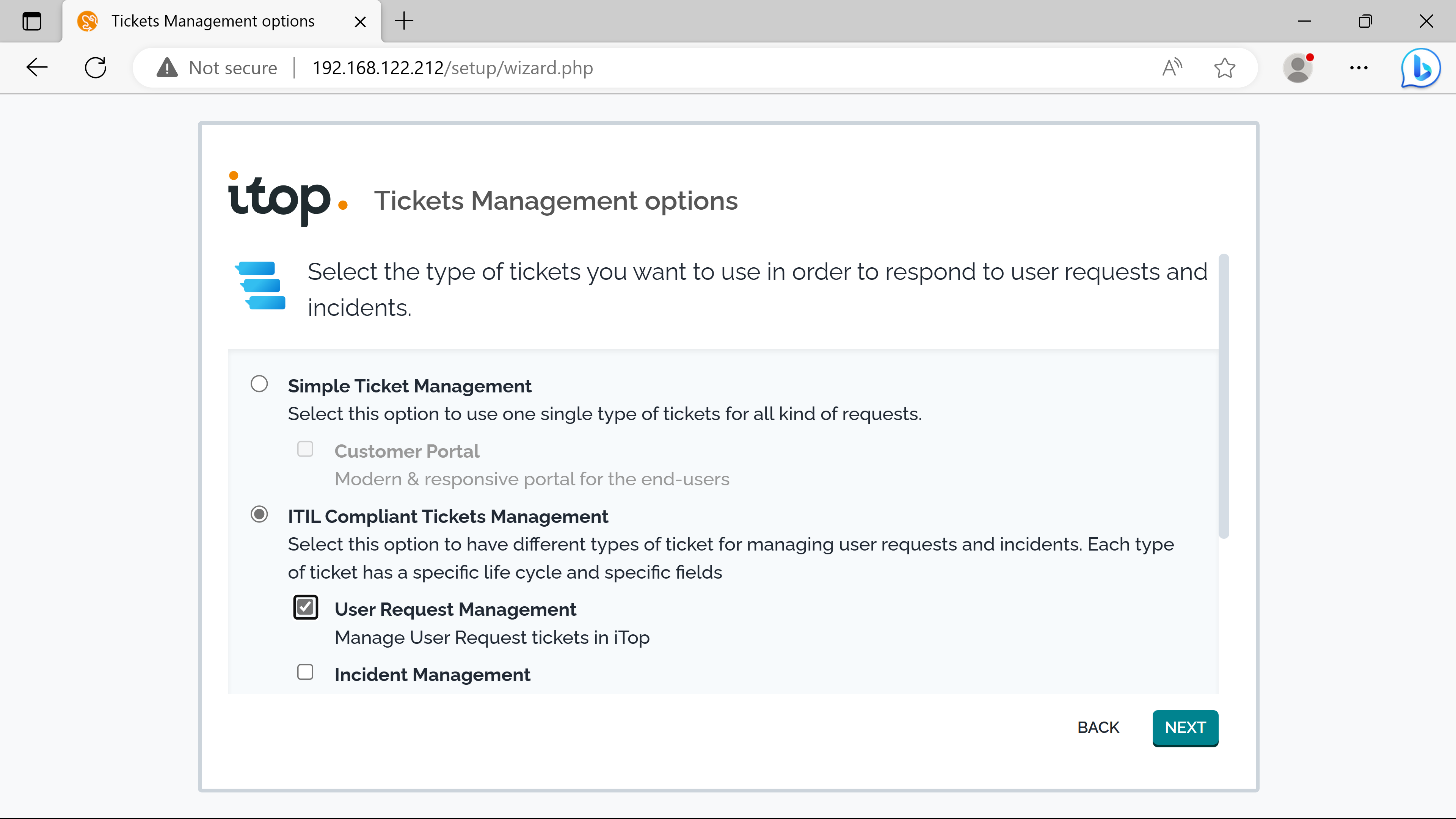
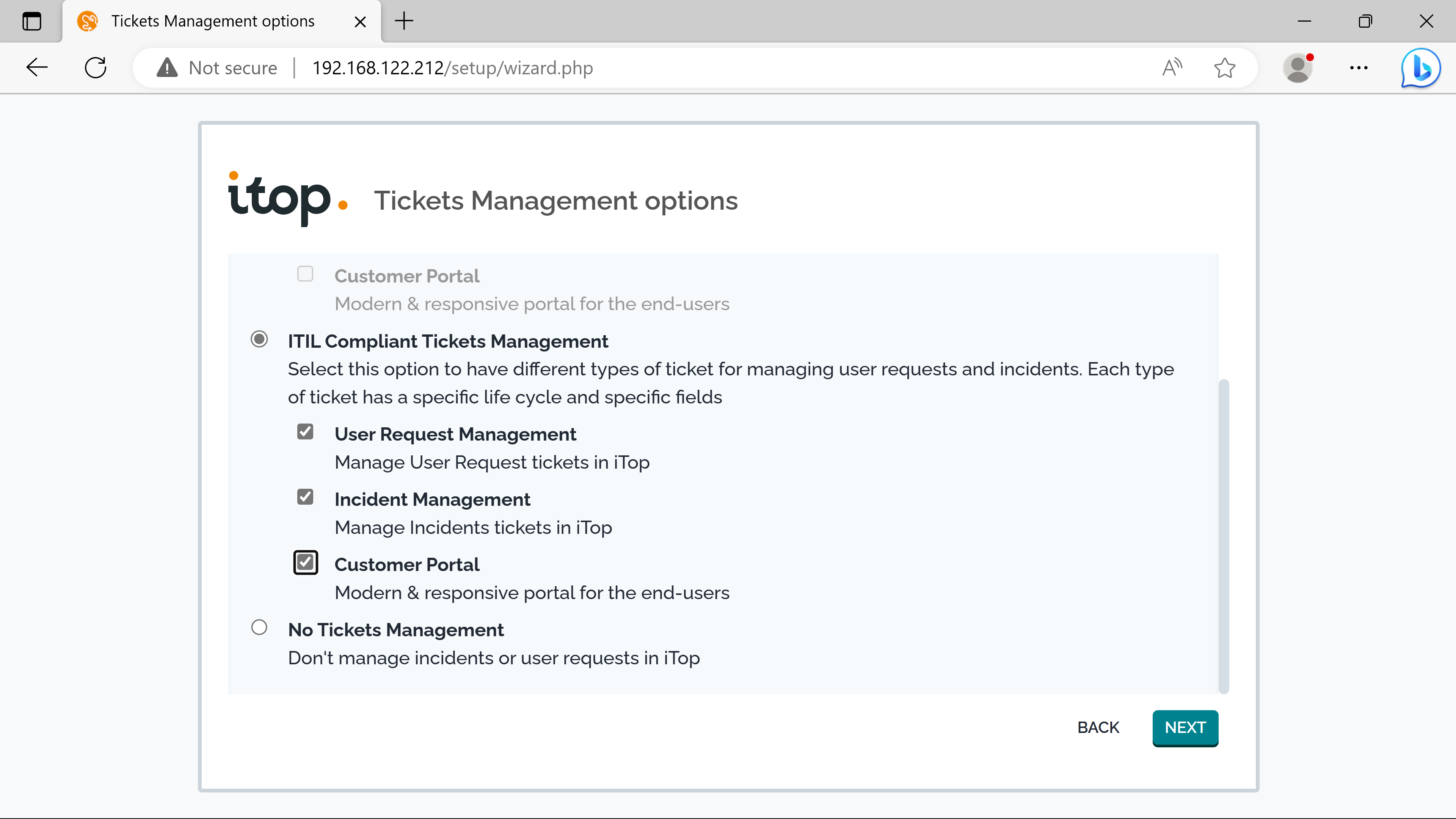
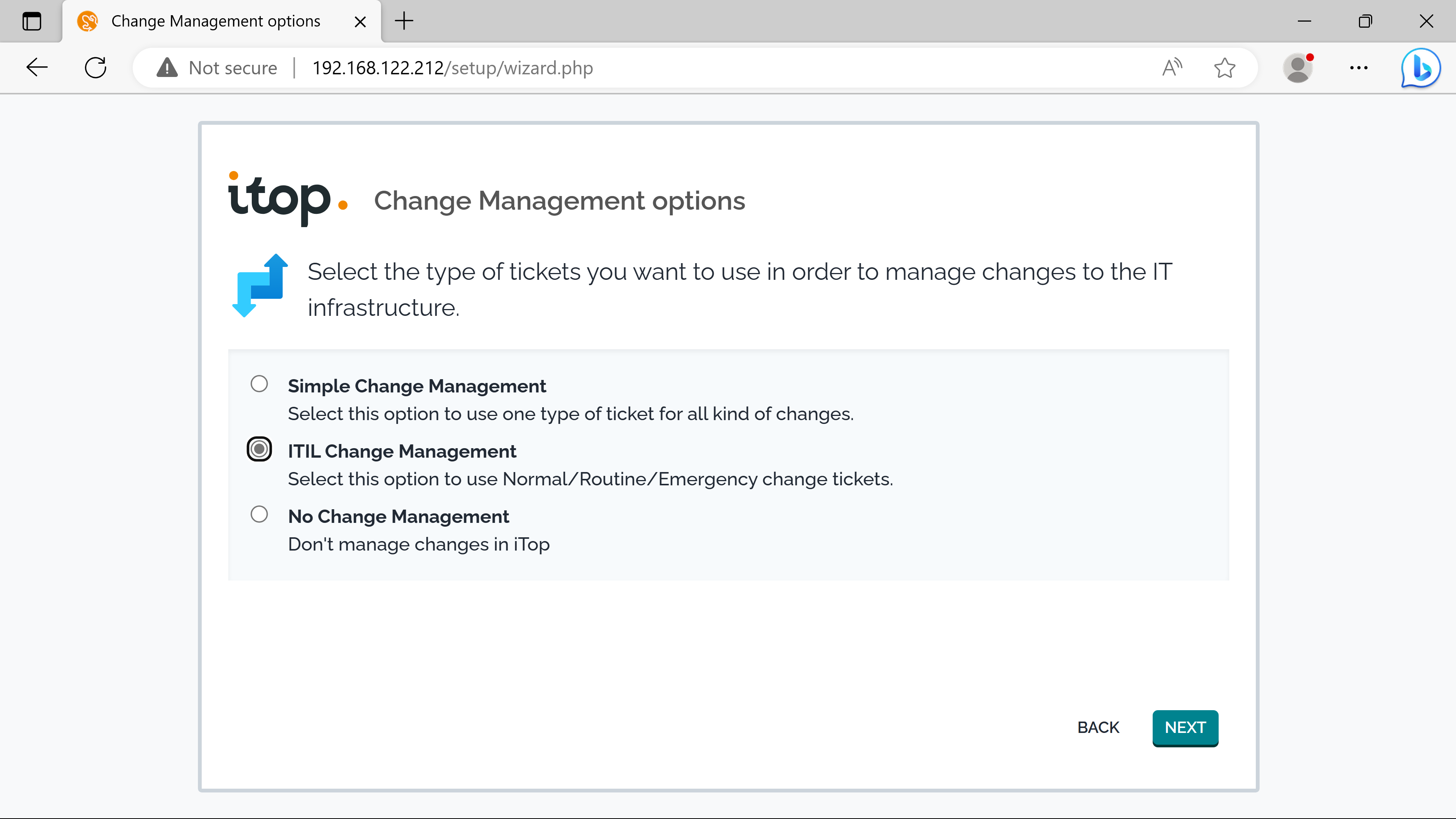
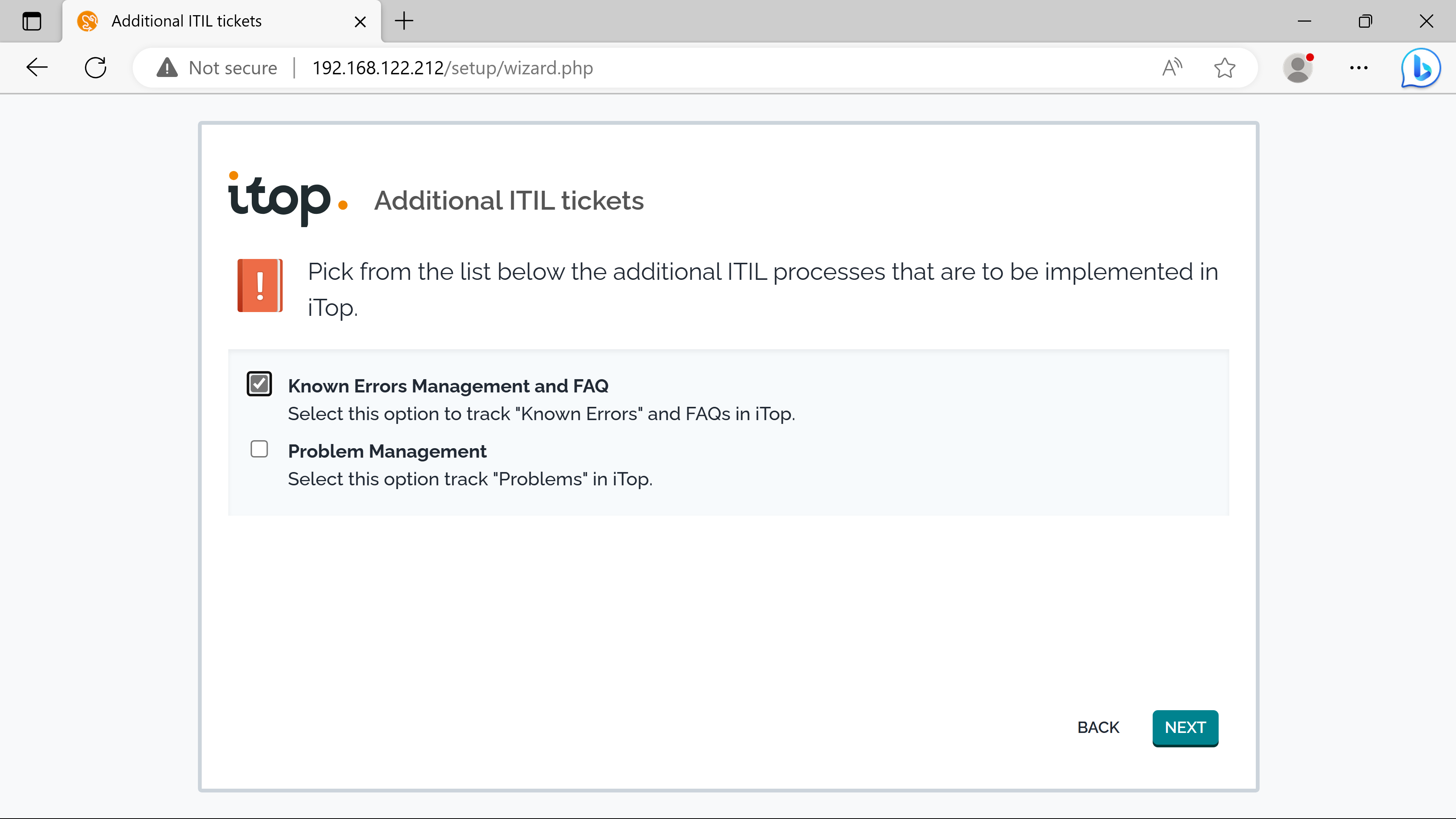
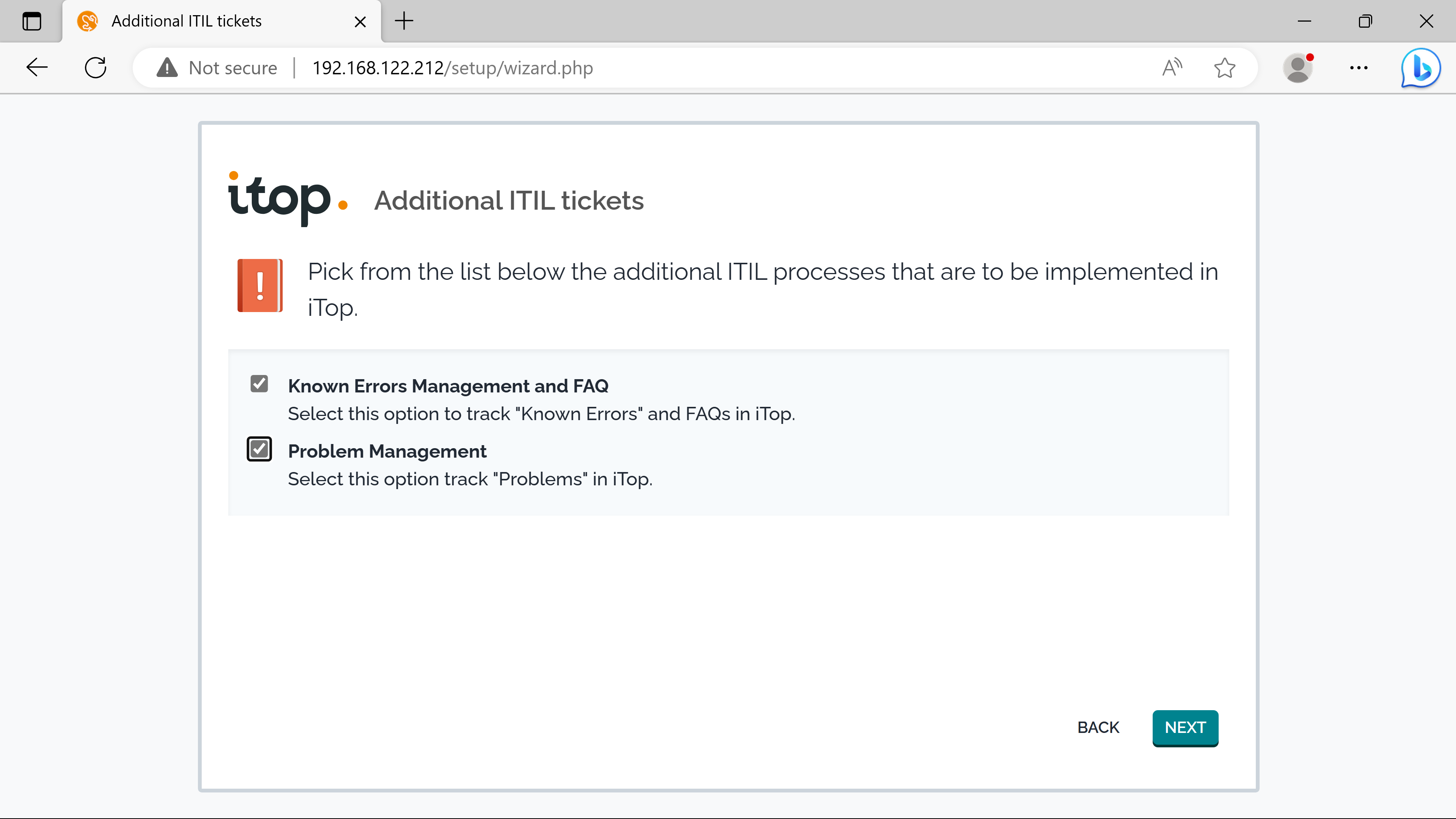
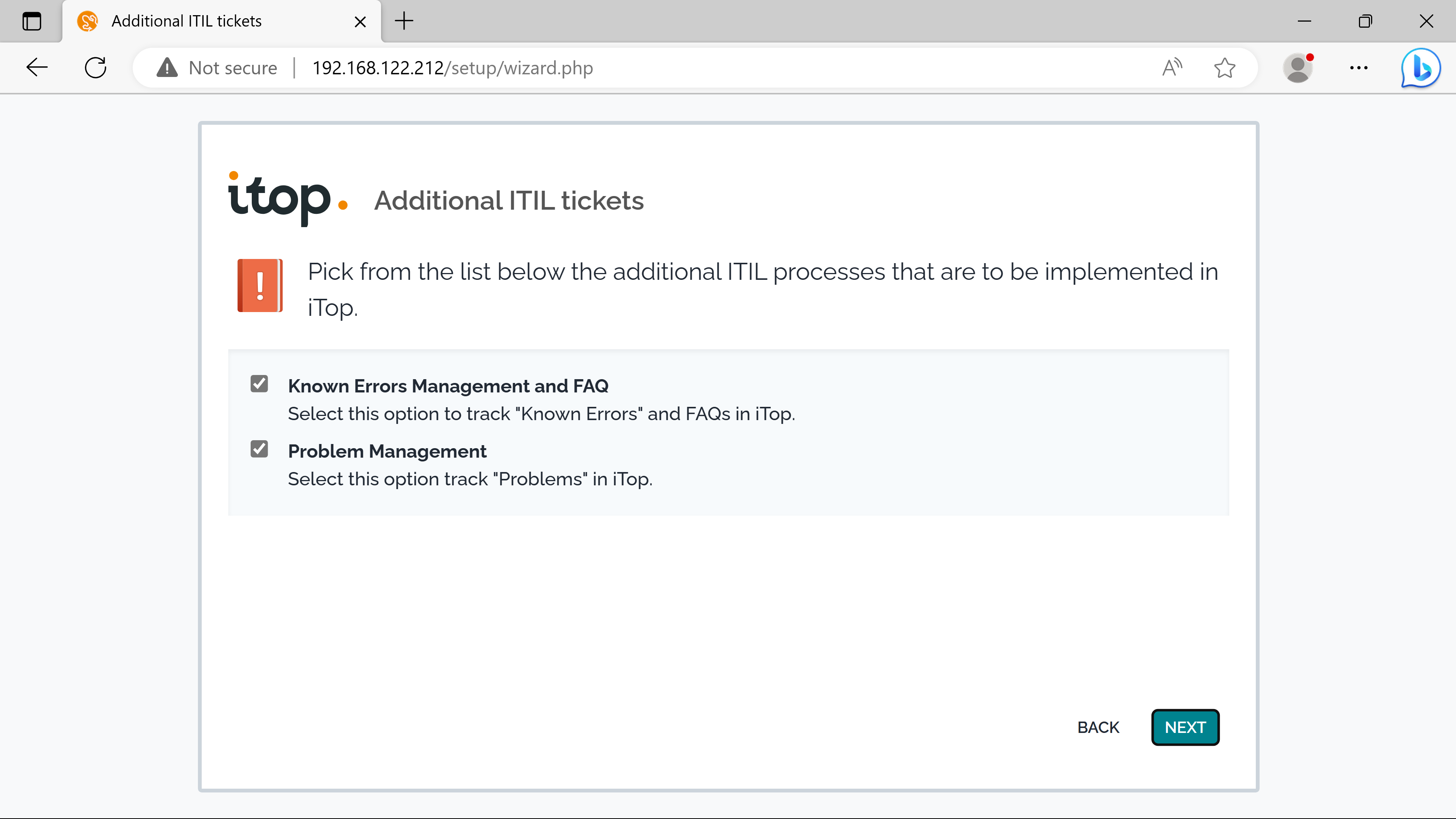
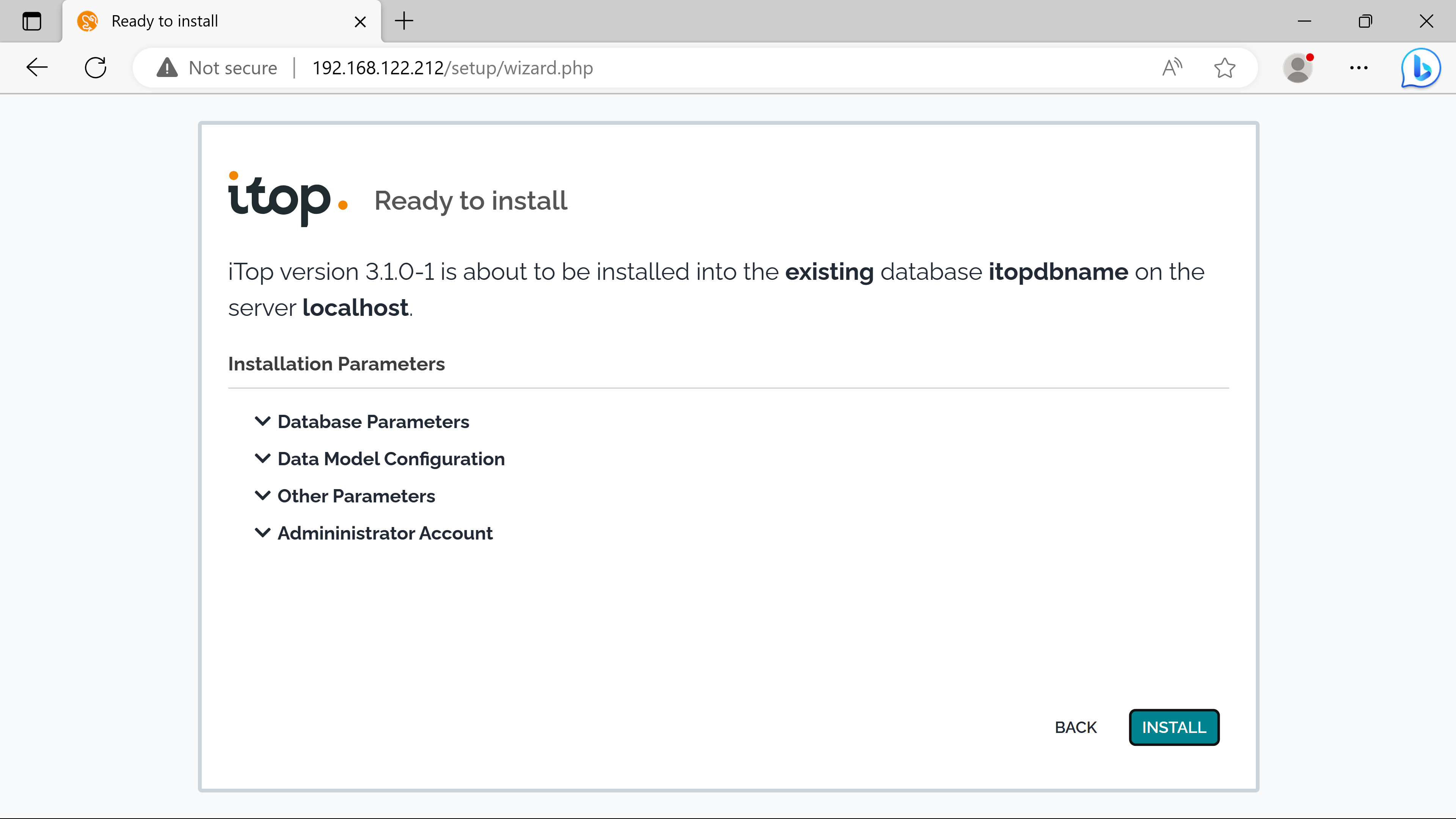
cmdb confirguration#
The cmdb (organizations, persons, teams etc.) needs to be configured first.
Depending on the company/ies & the infrastructure/s sizes, it could take some time to populate.
Exporting & importing csv files is a great option to configure it quickly. Here is a video from itop explaining how to do so (i still think putting mine will be worse).
Synchronizing csv files (itop server & an editor side) can also be done to avoid entering each modification manually, scheduling this task to. ELDAP & AD services can also be used instead of this method.
Manual objects implementation & modification can also be done. A rest api is also present for external use cases.
itsm overview#
The itsm is following the cmdb configuration: users created, teams, organizations, services, contracts etc.
External User profile for the iTop User object have a dashboard to create requests according to purchased services.
The user can change his Phone number, Location according to his company’s locations in the cmdb, the language to use or his profile picture.
It can also rename his function inside the company or change his password.
When entering in New request, according to default objects, the services can be defined in sub-services to help the end user.
The provider has the itop dashboard (administrators like person c or other profiles) to interract with created tickets.
To avoid putting a gigantic amount of screenshots to show how the itsm works, here is itop video for that (better than the ones i made i think…).
A designer is available to custom the itsm interfaces.
monitoring#
Once the cmdb is configured, links can be done between hardware & Application Services for the end users.
They are created using Contracts (Customer & Provider) with SLAs etc.
Since itop is an itsm & cmdb solution, it doesn’t have a proper monitoring system.
However, itop can integrate nagios for incident management (creating tickets).
close#
It required a lot of time & effort to make my hands on, it’s not incredibly difficult - depends on what you usually do - but demanding. (compare to the nagios experience i have)
To keep their customers’ time, they do bootcamps for 140$/h & have paid consultants.
For a production or business use, customers may pay for the professional or business itop solutions with consultants to help them integrating itop & keep a lot of time.
I think one or more IT guys are needed to implement, maintain & using it (expecially with oql querries & various technos not covered).
I saw on forums itop could implement customers’ itsm for their need, but the discussion stopped here.
I also like their blog.
I am happy that i have found a way to understand itop & the surroundings properly & alone in a week, i hope so.